5.1 KiB
myst
| myst | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
:orphan:
AMD RDNA2 system optimization
Workstation workloads
Workstation workloads, much like those for HPC, have a unique set of requirements: a blend of both graphics and compute, certification, stability and others.
The document covers specific software requirements and processes needed to use these GPUs for Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) and machine learning tasks.
The main purpose of this document is to help users utilize the RDNA™ 2 GPUs to their full potential.
:header-rows: 1
:stub-columns: 1
* - System Guide
- Architecture reference
- White papers
* - [System settings](#system-settings)
- [AMD RDNA 2 instruction set architecture](https://www.amd.com/system/files/TechDocs/rdna2-shader-instruction-set-architecture.pdf)
- [RDNA 2 architecture](https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/rdna2-explained-radeon-pro-W6000.pdf)
System settings
This chapter reviews system settings that are required to configure the system
for ROCm virtualization on RDNA2-based AMD Radeon™ PRO GPUs. Installing ROCm on
Bare Metal follows the routine ROCm
{doc}installation procedure<rocm-install-on-linux:install/install-methods/package-manager-index>.
To enable ROCm virtualization on V620, one has to setup Single Root I/O
Virtualization (SR-IOV) in the BIOS via setting found in the following
({ref}bios-settings). A tested configuration can be followed in
({ref}os-settings).
:::{attention} SR-IOV is supported on V620 and unsupported on W6800. :::
(bios-settings)=
System BIOS settings
:header-rows: 1
:name: v620-bios
*
- Advanced / North Bridge Configuration
- IOMMU
- Enabled
- Input-output Memory Management Unit
*
- Advanced / North Bridge Configuration
- ACS Enable
- Enabled
- Access Control Service
*
- Advanced / PCIe/PCI/PnP Configuration
- SR-IOV Support
- Enabled
- Single Root I/O Virtualization
*
- Advanced / ACPI settings
- PCI AER Support
- Enabled
- Advanced Error Reporting
To set up the host, update SBIOS to version 1.2a.
(os-settings)=
Operating system settings
:header-rows: 1
:name: v620-prereq
*
- Server
- [SMC 4124](https://www.supermicro.com/en/Aplus/system/4U/4124/AS-4124GS-TNR.cfm) [AS -4124GS-TNR]
*
- Host OS
- Ubuntu 20.04.3 LTS
*
- Host Kernel
- 5.4.0-97-generic
*
- CPU
- AMD EPYC 7552 48-Core Processor
*
- GPU
- RDNA2 V620 (D603GLXE)
*
- SBIOS
- Version SMC_r_1.2a
*
- VBIOS
- 113-D603GLXE-077
*
- Guest OS 1
- Ubuntu 20.04.5 LTS
*
- Guest OS 2
- RHEL 9.0
*
- GIM Driver
- gim-dkms_1.0.0.1234577_all
*
- VM CPU Cores
- 32
*
- VM RAM
- 64 GB
Install the following Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) Hypervisor packages:
sudo apt-get -y install qemu-kvm qemu-utils bridge-utils virt-manager gir1.2-spiceclientgtk* gir1.2-spice-client-gtk* libvirt-daemon-system dnsmasq-base
sudo virsh net-start default /*to enable Virtual network by default
Enable input-output memory management unit (IOMMU) in GRUB settings by adding the following line to /etc/default/grub:
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet splash" for AMD CPU
Update grub and reboot
sudo update=grub
sudo reboot
Install the GPU-IOV Module (GIM, where IOV is I/O Virtualization) driver and follow the steps below.z
sudo dpkg -i <gim_driver>
sudo reboot
# Load Host Driver to Create 1VF
sudo modprobe gim vf_num=1
# Note: If GIM driver loaded successfully, we could see "gim info:(gim_init:213) *****Running GIM*****" in dmesg
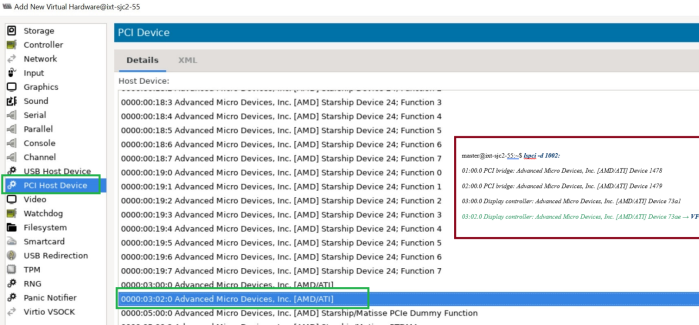
lspci -d 1002:
Which should output something like:
01:00.0 PCI bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD/ATI] Device 1478
02:00.0 PCI bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD/ATI] Device 1479
03:00.0 Display controller: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD/ATI] Device 73a1
03:02.0 Display controller: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD/ATI] Device 73ae → VF
Guest OS installation
First, assign GPU virtual function (VF) to VM using the following steps.
-
Shut down the VM.
-
Run
virt-manager -
In the Virtual Machine Manager GUI, select the VM and click Open.
-
In the VM GUI, go to Show Virtual Hardware Details > Add Hardware to configure hardware.
-
Go to Add Hardware > PCI Host Device > VF and click Finish.
Then start the VM.
Finally install ROCm on the virtual machine (VM). For detailed instructions,
refer to the {doc}Linux install guide<rocm-install-on-linux:install/install-methods/package-manager-index>.