ZusK
First touch point of Blockchain Powered eSIM
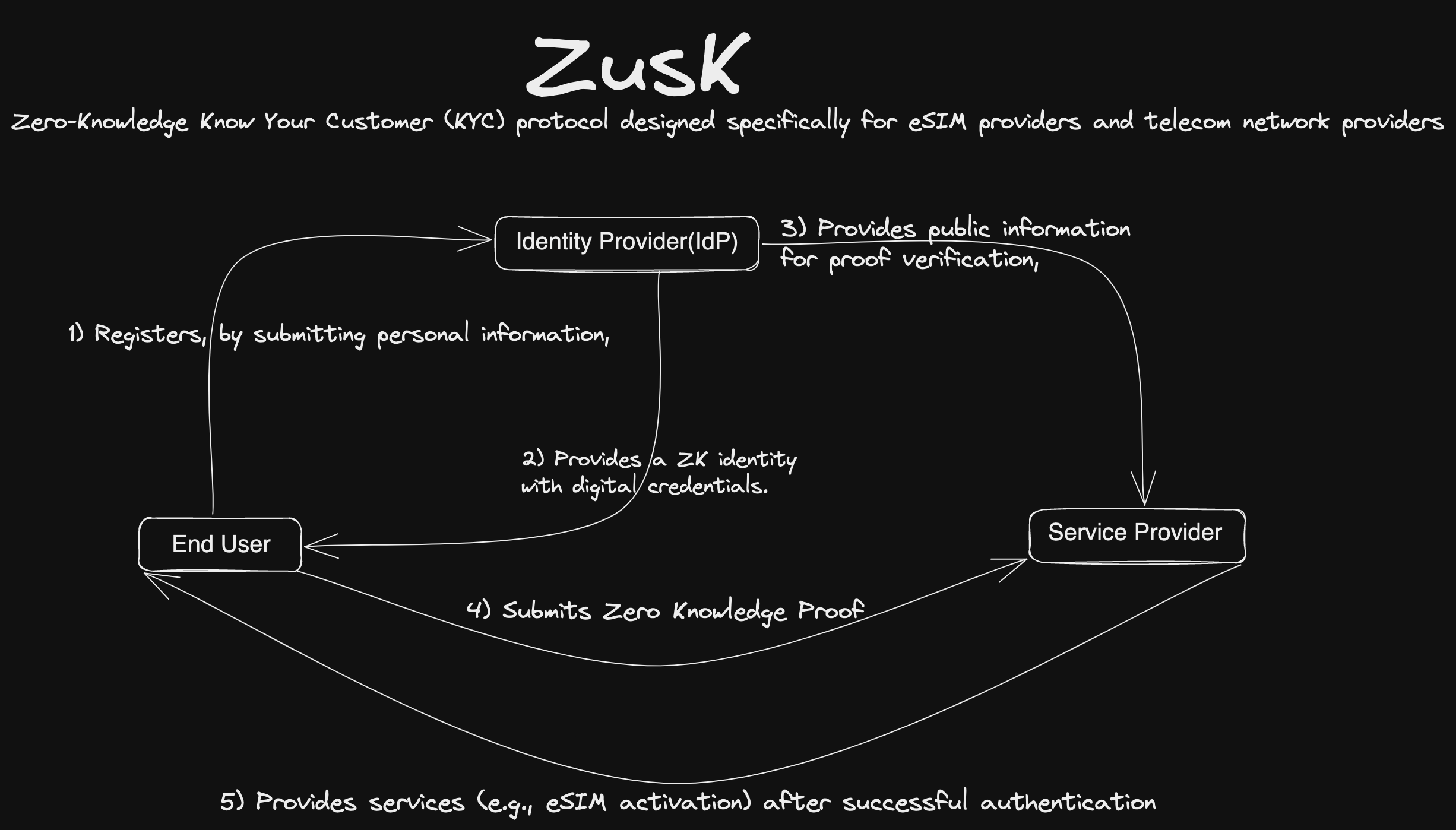
Zusk is a Zero-Knowledge Know Your Customer (KYC) protocol designed specifically for eSIM providers and telecom network providers.
It aims to verify the validity of users while preserving their privacy and maintaining compliance with KYC requirements.
Zusk leverages zero-knowledge cryptographic algorithms to create a ZK identity for end users, enabling them to undergo KYC checks through a zero-knowledge proof protocol.
Roles of Different Personas:
a. End User/Customer:
- Registers and submits personal information with the IdP.
- Receives a ZK identity and digital credentials.
- Uses ZK identity to generate zero-knowledge proofs when interacting with service providers.
b. Identity Provider (IdP):
- Processes end user's personal information and performs initial KYC.
- Generates a ZK identity and digital credentials for the end user.
- Stores encrypted representations of the user's data securely.
- Provides public information to service providers for proof verification.
c. eSIM Providers and Telecom Network Providers (Service Providers):
- Implement the Zusk protocol to support zero-knowledge proofs.
- Receive and verify zero-knowledge proofs submitted by end users.
- Provide services (e.g., eSIM activation) to users after successful authentication.
Zusk Protocol Workflow
The Zusk protocol workflow can be summarized in the following steps:
a. User Enrollment:
- The end user registers with the IdP and submits personal information.
- The IdP performs the necessary KYC checks and generates a ZK identity and digital credentials for the user.
b. Zusk Protocol Integration:
- Service providers (e.g., eSIM providers and telecom network providers) integrate the Zusk protocol to support zero-knowledge proofs.
c. User Authentication:
- The end user generates a zero-knowledge proof using their ZK identity and digital credentials.
- The end user submits the zero-knowledge proof to the service provider (e.g., Airalo) as part of the authentication process.
- The service provider verifies the proof using the public information provided by the IdP and the Zusk protocol.
- If the proof is successfully verified, the service provider proceeds with providing the requested service (e.g., eSIM activation).
By implementing the Zusk protocol, eSIM providers and telecom network providers can offer a privacy-preserving and secure KYC process to their customers while maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements. This approach allows users to authenticate their identity without exposing sensitive personal information, ensuring a higher level of privacy and security.
More about IdP:
Identity Provider (IdP) is a crucial component in the Zusk system, responsible for securely managing user identities and performing initial KYC checks. The IdP creates and manages users' Zero-Knowledge (ZK) identities and digital credentials, enabling them to generate and submit zero-knowledge proofs when interacting with service providers.
Structure of the Identity Provider (IdP):
Registration and User Onboarding:
The IdP provides a platform for users to register and submit their personal information required for KYC purposes. This could include details such as name, date of birth, address, and identification documents (e.g., Aadhar card, passport, driver's license).
KYC Verification:
Once the user submits their information, the IdP performs necessary KYC checks to validate the user's identity. This may involve cross-referencing the provided information with external databases, government records, or other trusted sources.
Cryptographic Processing and ZK Identity Creation:
Upon successful KYC verification, the IdP uses cryptographic techniques to generate encrypted representations of the user's personal data. These encrypted representations form the basis of the user's ZK identity. The IdP also issues digital credentials linked to the user's ZK identity, which are signed by the IdP to ensure their authenticity.
Secure Storage:
The IdP securely stores the encrypted representations of users' personal data, ensuring that only authorized parties can access this information.
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI):
The IdP maintains a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) to facilitate the verification of zero-knowledge proofs. The IdP's public key, along with other relevant public information, is shared with service providers so they can verify the authenticity of the zero-knowledge proofs submitted by users.
Integration with Service Providers:
The IdP provides APIs, SDKs, or other integration tools to enable service providers (e.g., eSIM providers and telecom network providers) to implement the Zusk protocol and support zero-knowledge proofs.
IdP plays a central role in the Zusk system by securely managing user identities, performing KYC checks, creating ZK identities and digital credentials, and facilitating the verification of zero-knowledge proofs. By doing so, the IdP enables a secure and privacy-preserving authentication process for users interacting with service providers.
Previous Approach
A Zero-Knowledge Know Your Customer(KYC) protocol that is specifically designed for telecom network providers/companies to verify users who want to subscribe to their network. ZusK uses zero-knowledge cryptographic algorithms to create a ZK identity for end users/customers and perform KYC using a zero-knowledge proof protocol.
ZusK Design and Architecture
The ZusK protocol aims to provide a secure and privacy-preserving KYC process for telecom network providers while verifying users who want to subscribe to their network. The protocol utilizes three factors for user authentication: biometrics, a personal identification number (PIN), and a private key (PK). The user's mobile number will serve as the public key for identification purposes.
Architecture componenets:
-
Trusted Third Party (TTP): The TTP is responsible for creating a unique digital identity for the customer and encrypting it using a one-way hash function. The TTP also provides the zero-knowledge proof protocol for end users/customers to prove that they possess the private key to their encrypted digital identity.
-
Company: The company generates a random challenge for the customer, which requires them to prove that they possess the private key to their encrypted digital identity. The company then verifies the zero-knowledge proof provided by the customer and proceeds with the KYC process.
-
End User/Customer: The end user/customer provides their identity information to the TTP, which is used to create a unique digital identity for the customer.
ZusK Workflow
User Registration
a. The user submits their biometric data (e.g., fingerprint, facial scan) to a trusted third-party biometric authentication service (BAS).
b. The BAS generates a unique biometric identifier (BI) for the user and securely stores the user's biometric data, associating it with the BI.
c. The user creates a PIN and generates a public-private key pair (PPK). The mobile number serves as the public key.
d. The user generates a zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) that attests to the correctness of their biometric data, PIN, and PPK without revealing the actual data.
e. The user sends the ZKP, BI, and their mobile number (public key) to the telecom network provider.
Telecom Network Provider Verification
a. The telecom network provider forwards the ZKP, BI, and mobile number to the BAS for verification.
b. The BAS verifies the ZKP against the stored biometric data and responds with a confirmation of validity.
c. If the verification is successful, the telecom network provider creates an account for the user and associates it with the mobile number (public key).
User Subscription
a. To subscribe to the network, the user needs to authenticate themselves using their biometric data, PIN, and PK.
b. The user generates a new ZKP that proves they possess the correct biometric data, PIN, and PK without revealing them.
c. The user sends the ZKP, their mobile number (public key), and their desired subscription package to the telecom network provider.
d. The telecom network provider verifies the ZKP and, if successful, activates the subscription for the user.
Ongoing Authentication
a. To ensure secure and continuous access to the network, the user periodically generates new ZKPs as a form of ongoing authentication.
b. The telecom network provider verifies these ZKPs and maintains the user's access to the network.
AIM
ZusK is aiming to become a secure and efficient KYC protocol that uses zero-knowledge proofs to verify the identity of end users/customers. It is designed to provide a decentralized and privacy-enhancing solution for telecom network providers/companies to verify the identity of their customers without collecting or storing their personal information. ZusK is the first touch point of the project "Blockchain Powered eSIM" which aims to provide end users with a novel way of using eSIM services that enables them to do more than just communicate, and also provides users the option to use a network without trusting the network provider.