2.6 KiB
FIXME(Arthur): explain recent updates on the fusing
Fusing Floating Point Operations
Why is it needed?
The current compiler stack only supports integers with 7 bits or less. But it's not uncommon to have numpy code using floating point numbers.
We added fusing floating point operations to make tracing numpy functions somewhat user friendly to allow in-line quantization in the numpy code e.g.:
import numpy
def quantized_sin(x):
# from a 7 bit unsigned integer x, compute z in the [0; 2 * pi] range
z = 2 * numpy.pi * x * (1 / 127)
# quantize over 6 bits and offset to be >= 0, round and convert to integers in range [0; 63]
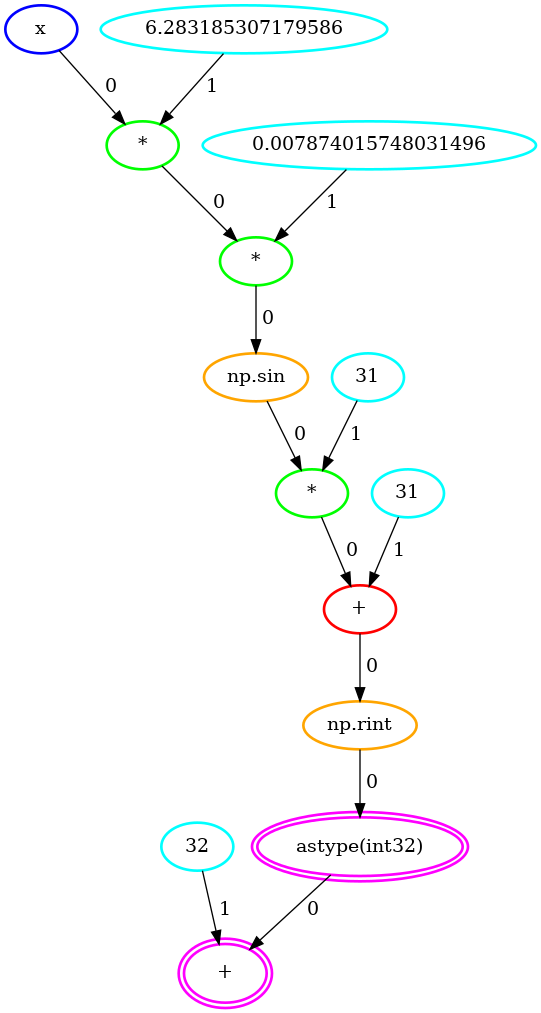
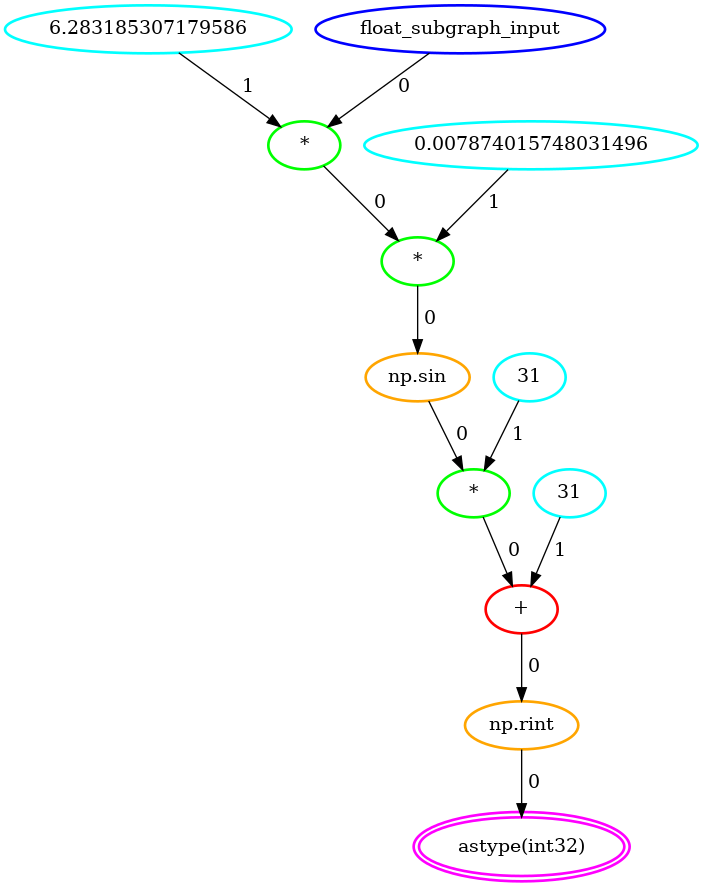
quantized_sin = numpy.rint(31 * numpy.sin(z) + 31).astype(numpy.int32)
# output quantized_sin and a further offset result
return quantized_sin, quantized_sin + 32
This function quantized_sin is not strictly supported as is by the compiler as there are floating point intermediate values. However, when looking at the function globally we can see we have a single integer input and a single integer output. As we know the input range we can compute a table to represent the whole computation for each input value, which can later be lowered to a PBS in the FHE world.
Any computation where there is a single variable integer input and a single integer output can be replaced by an equivalent table look-up.
The quantized_sin graph of operations:
The float subgraph that was detected:
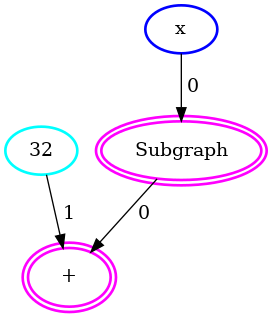
The simplified graph of operations with the float subgraph condensed in an GenericFunction node:
How is it done in Concrete?
The first step consists in detecting where we go from floating point computation back to integers. This allows to identify the potential terminal node of the float subgraph we are going to fuse.
From the terminal node, we go back up through the nodes until we find nodes that go from integers to floats. If we can guarantee the identified float subgraph has a single variable integer input then we can replace it by an equivalent GenericFunction node.
An example of a non fusable computation with that technique is:
import numpy
def non_fusable(x, y):
x_1 = x + 1.5 # x_1 is now float
y_1 = y + 3.4 # y_1 is now float
add = x_1 + y_1
add_int = add.astype(numpy.int32)
return add_int
From add_int you will find two Add nodes going from int to float (x_1 and y_1) which we cannot represent with a single input table look-up.